With the rapid development of LED technology and the continuous improvement of light efficiency, LED spotlight technology is also developing rapidly. The current LED spotlights are almost the replacement of traditional tungsten halogen lamps. Compared with traditional lamps, LED spotlights have significant advantages in terms of energy saving and long life. With the reduction of the cost of LED spotlights, the application of LED spotlights has gradually begun to spread. This article will briefly introduce and consider the technical requirements of LED spotlights, the specifications and types of common LED spotlights, the structure of LED spotlights, the common sense of LED spotlights, and the development direction of LED spotlights.
First, LED spotlight technical requirements
At present, LED spotlights mainly replace traditional tungsten halogen lamps. Most of the relevant safety requirements refer to traditional lighting requirements, and according to the characteristics of LED lamps, a set of safety certification standards has been formed. At present, in the certification of LED spotlights, the international standards mainly include European CE and North American UL certification, and voluntary certification (CQC) is available in China.
The CE certification includes both LVD and EMC, of ​​which LVD is implemented in accordance with EN60968 (IEC 62560 will be upgraded); EMC is implemented in accordance with EN55015, EN61547, EN61000-3-2 and EN61000-3-3. In addition, LED lamps usually require additional reference to IEC 62471 for photobiosafety testing. In North America, UL safety and FCC EMC certification are usually required. UL implementation standards are UL1993, UL8750 and UL1310; FCC implementation standards are FCC PART15 Subpart B. In China, the use of voluntary certification (CQC) for LED spotlights, the implementation standards are GB24906-2010 (safety) and GB 17743-2007 (electromagnetic compatibility).
In addition, there are many standard regulations on the performance of LED spotlights. ENERGY STAR has relevant requirements in the United States; China has energy-saving certification requirements, and the implementation standard is CQC 3129-2010. Among these requirements, the color temperature, color rendering index, initial luminous flux, luminous efficacy, luminous flux maintenance rate, life, center light intensity, nominal power, power factor, and product identification of the LED spotlight are specified.
The lifespan of many electronic products is judged by broken, but LED is a long-life light source that can be used for a long time without damage. However, the output of the luminous flux decays with time. Therefore, the time required for the light to decay to 70% is usually defined in the industry to define the life of the LED light source, that is, L70. With the advancement of technology, the light decay of LEDs is getting slower and slower, and it is difficult to fully test the time of light decay to 70%. Since the life of electronic products is exponential, LEDs usually undergo aging for a short period of time. By sampling the light decay data and then estimating the light decay to 70% by exponential function, the formula is as follows:

Generally, the luminescence maintenance rate LM (Lumen Maintains) is 6,000 hours for LED aging. According to the exponential law, if LM >91.8% after 6000 hours, it can claim 25,000 hours of life. If LM>94.1% can claim 35,000 hours of life, However, the life calculation time does not exceed 6 times the test time.

Figure 1. Light decay index curve
The angle of the LED spotlight is generally defined by the beam angle of 50% peak intensity. Figure 2 is a polar coordinate light intensity distribution curve of an LED spotlight. It can be seen that the angle corresponding to 50% light intensity is about ±20°, so the angle of this spotlight is 40°.

Figure 2. Polarized light intensity distribution curve of LED spotlight
Second, the specifications and types of common LED spotlights
At present, the LED spotlights mainly replace the traditional tungsten halogen lamps, so the external dimensions refer to the IEC 60630 standard, and the lamp heads refer to the IEC 60061-1 standard. According to the traditional spotlights, the current LED spotlights mainly include MR16, PAR16, PAR20, PAR30, and PAR38. Among them, MR16 usually adopts GU5.3 lamp holder; PAR16 mainly adopts GU10, E26 (America)/E27 (Europe and China) and E14 lamp holders; PAR20/PA30/PAR38 mainly adopts E26 and E27 lamp holders.

Figure 3. Various lamp holders (E14, E17, E26, E27, GU10, GU5.3 from left to right)
Third, the structure of common LED spotlights
The current LED spotlights are self-ballasted, that is, the LED drive power supply is all built in the inside of the lamp body, and can be used directly after being powered on.
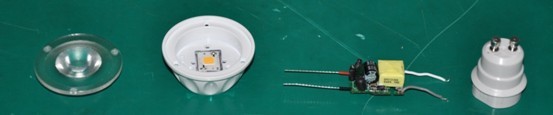
Figure 4. LED spotlight (PAR16-GU10) disassembly diagram
As shown in the above figure, the spotlight disassembly diagram can be seen that the current LED spotlights are mainly composed of optical components (lenses, reflectors), LED light sources, heat sinks, drive power supplies, and lamp caps. However, LED spotlights of various manufacturers, due to the different materials, processes, and LED packaging methods, make the spotlights have some differences in design and processing.
1. LED light source and optical device
The current LED spotlights are mainly made of multiple high-power LEDs and integrated package LEDs, as shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.

Figure 5. Multiple high-power LEDs . Figure 6. Integrated package LED spotlights.
With multiple high-power LEDs, a single board is usually required to electrically connect the LEDs. The board is mostly made of aluminum substrate (MCPCB); for some designs, it is also made of fiberglass (FR-4), but it needs to be specially designed for thermal pad. Then fix it to the lamp housing heat sink with screws or glue. A number of high-power LED spotlights, the lens is usually used to independently align each LED, and then combined into a spot lens.
Spotlights made with integrated packaged LEDs do not require a circuit board and can be directly connected to the LED output. It is also fixed to the lamp housing heat sink by screws or glue. The secondary optics of the spotlights usually use a lens or a reflector to distribute light. The height of the lens and the reflector are high, and the light distribution at a small angle is difficult.
In addition, for large-area spotlights, the secondary light distribution design of the entire luminaire is mostly completed by a combination of multiple optical components, as shown in FIG.

Figure 7. Spotlights with multiple optics combinations