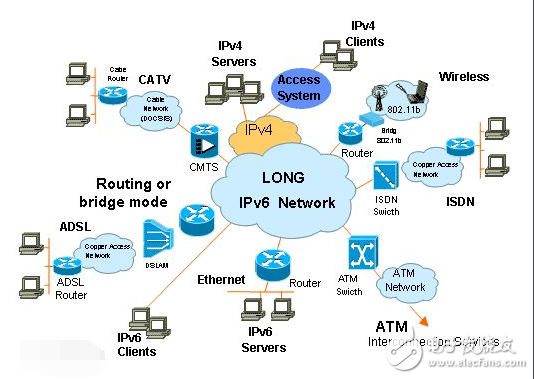
IPv6 is an abbreviation of Internet Protocol Version 6, in which Internet Protocol is translated as "Internet Protocol." IPv6 is a next-generation IP protocol designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to replace the current version of the IP protocol (IPv4). It claims to be able to compile a URL for every grain of the world.
The biggest problem with IPv4 is the limited network address resources, which seriously restricts the application and development of the Internet. The use of IPv6 not only solves the problem of the number of network address resources, but also solves the obstacles for multiple access devices to connect to the Internet.
Composition
display method
The IPv6 address length is 128b, which is four times the length of the IPv4 address. Therefore, the IPv4 dotted decimal format is no longer applicable, and is expressed in hexadecimal. There are three ways to represent IPv6.
First, the hexadecimal notation
The format is X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X, where each X represents 16b in the address, expressed in hexadecimal, for example:
ABCD: EF01: 2345: 6789: ABCD: EF01: 2345: 6789
In this notation, the leading zero of each X can be omitted, for example:
2001:0DB8:0000:0023:0008:0800:200C:417A→2001:DB8:0:23:8:800:200C:417A
Second, 0-bit compression representation
In some cases, an IPv6 address may contain a long period of 0, which can compress a consecutive segment of 0 into "::". However, to ensure the uniqueness of address resolution, "::" in the address can only appear once, for example:
FF01:0:0:0:0:0:0:1101 → FF01::1101
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 → ::1
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 → ::
Third, embedded IPv4 address notation
In order to implement IPv4-IPv6 interworking, the IPv4 address is embedded in the IPv6 address. In this case, the address is often expressed as: X:X:X:X:X:X:dddd, the first 96b is represented by a hexadecimal notation, and the last 32b The address is expressed in dotted decimal notation of IPv4. For example: 192.168.0.1 and ::FFFF:192.168.0.1 are two typical examples. Note that in the first 96b, the method of compressing 0 bit is still applicable [3].
Message content
The overall structure of an IPv6 packet is divided into an IPv6 header, an extended header, and an upper layer protocol data. The IPv6 header is a mandatory packet header. The length is fixed to 40B and contains the basic information of the packet. The extended header is an optional header. There may be 0, 1 or more. The IPv6 protocol implements various enrichments by extending the header. The upper layer protocol data is the upper layer data carried in the IPv6 packet, and may be an ICMPv6 packet, a TCP packet, a UDP packet, or other possible packets.
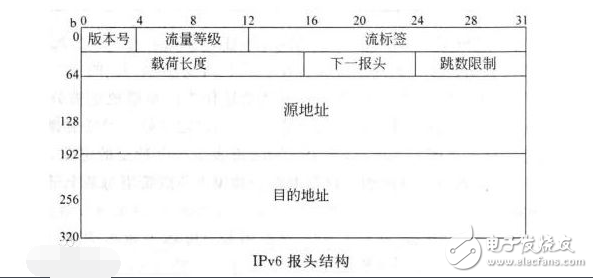
The packet header structure of IPv6 is as follows:
3.1 What are the significant advantages of IPv6 over IPv4?
Compared to IPv4, IPv6 has the following significant advantages:
(1) The address capacity is greatly expanded, from the original 32-bit to 128-bit, completely solve the problem of insufficient IPv4 address; support hierarchical address structure, which is easier to address; extended support for multicast and anycast address, which makes data A package can be sent to any one or a group of nodes;
(2) The large-capacity address space can truly realize the automatic configuration of stateless addresses, enabling IPv6 terminals to quickly connect to the network without manual configuration, realizing true plug-and-play;
(3) The header format is greatly simplified, thereby effectively reducing the processing overhead of the router or the switch to the header, which is very advantageous for designing a router or switch for processing the hardware header;
(4) Enhanced support for extended headers and options, which not only makes forwarding more efficient, but also provides full support for future network loading of new applications;
(5) The use of flow labels allows us to provide personalized network services for the types of data packets and to effectively guarantee the quality of service for related services;
(6) Authentication and privacy: IPv6 uses IPSec as a mandatory protocol to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of end-to-end communication at the network layer;
(7) IPv6 has many improvements in mobile networks and real-time communications. In particular, unlike IPv4, IPv6 has powerful auto-configuration capabilities that simplify system management for mobile hosts and local area networks.
3.2 Header structure
3.2.1 What is the header structure of IPv6?
The structure of the new IPv6 header is much simpler than that of IPv4. The IPv6 header removes many of the less common domains in the IPv4 header and puts them into optional and header extensions; the options in IPv6 have stricter definitions. There are 10 fixed-length domains, 2 address spaces, and several options in IPv4. There are only 6 domains and 2 address spaces in IPv6.
Although the IPv6 header occupies 40 bytes, which is 1.6 times that of the 24-byte IPv4 header, it does not need to consume excessive memory capacity because its length is fixed (the IPv4 header is long).
Header length, type of service (TOS), identifier (idenTIficaTIon), flag, fragment offset, and header checksum in IPv4 The fields are deleted. The name or part of the three fields of the total length, protocol type, and TIme to live (TTL) are changed. The option (opTIons) is completely changed. Two new ones have been added. Domain, which is the priority and flow label.
The figure below shows the specific IPv4 and IPv6 header comparison.
Table 1 IPv4 header format
4bit version number
4bit header length
8bit service type
16bit packet length
Identifier (16bit)
Logo (4bit)
Segment offset (12bit)
Time to live (8bit)
Transmission protocol (8bit)
Header checksum (16bit)
Source IP address (32bit)
Destination IP address (32bit)
Option (24bit)
Fill (8bit)
Table 2 ipv6 header format
4bit version number
4bit priority
24bit stream tag
Payload length (16bit)
Next header (8bit)
HOP limit (8bit)
Source IP address (128bit)
Destination IP address (128bit)
Waterproof relay is a common device in automatic control system. It is generally used to connect and disconnect the circuit. It is an important part of automatic control and remote control circuit.
Waterproof Relay,Miniature Waterproof Relay,Low Power Waterproof Relays,New Model Waterproof Relay
Ningbo Xingchuangzhi Electric Appliance Co.,Ltd. , https://www.xingchuangzhi.com