Let's start by understanding what a clock is. In a microcontroller, the clock is like its heart — it drives all operations and keeps every part of the system in sync. Think of it as the beat of a song when you're doing morning exercises. When you follow the rhythm, everyone moves together. The faster the beat, the quicker the actions; the slower the beat, the more relaxed the pace.
Now, what are internal and external clocks? Many PIC microcontrollers can use either an external clock source (like a 4MHz quartz crystal) or an internal RC clock. Some models even allow for multiple frequency options. For example, the PIC18LF1823 has an internal clock that can run up to 32MHz and as low as 31kHz. This flexibility helps reduce power consumption. While sleep modes are common for power saving, sometimes reducing the clock speed is a better option if the CPU still needs to perform tasks at a lower rate.
How do we set the clock? Typically, it involves two main components: the configuration word and the oscillator control register (OSCCON). Let’s take the PIC18LF1823 as an example. The FOSC bit in the configuration word determines whether the internal or external oscillator is used. The PLLEN bit enables the PLL (Phase-Locked Loop), which multiplies the clock frequency.
The OSCCON register controls the internal clock settings. If an external clock is used, this register is not needed. Here’s a detailed look at the OSCCON register from the datasheet:
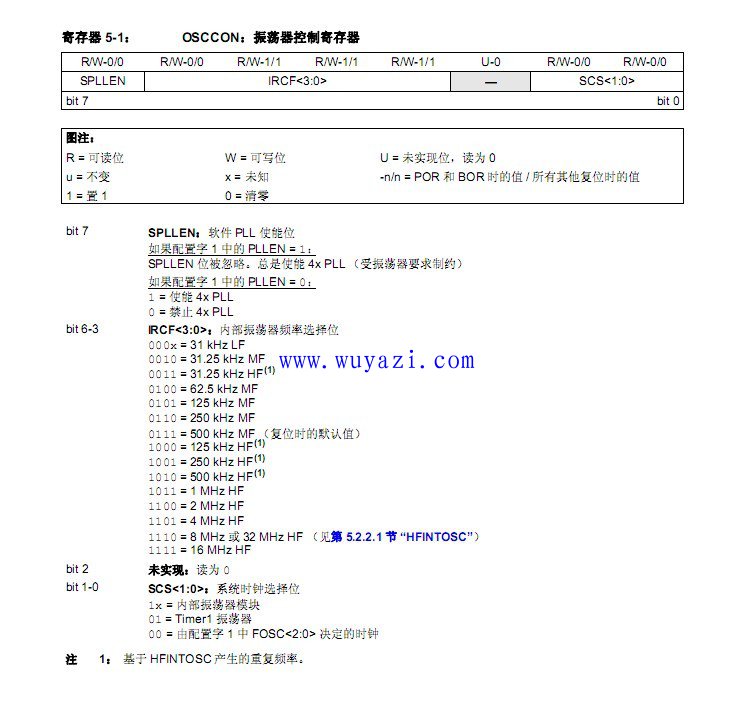
Example: Setting the clock to 8MHz using the internal oscillator
Development environment: MPLAB X IDE
Chip model: PIC18LF1823
#include <xc.h>
__CONFIG(FOSC_INTOSC & WDTE_OFF & PWRTE_ON & MCLRE_OFF & CP_ON & CPD_OFF & BOREN_ON &
CLKOUTEN_OFF & IESO_ON & FCMEN_ON);
__CONFIG(PLLEN_OFF & LVP_OFF); // Set FOSC to INTOSC
void init_fosc(void) {
OSCCON = 0x70; // Set internal clock to 8MHz
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
init_fosc();
while(1);
}
What is the PLL used for? It takes an 8MHz clock and multiplies it by four to produce 32MHz. Importantly, the PLL only works with an 8MHz input. Other frequencies won't work with it.
Example: Setting the clock to 32MHz using the internal oscillator
Development environment: MPLAB X IDE
Chip model: PIC18LF1823
#include <xc.h>
__CONFIG(FOSC_INTOSC & WDTE_OFF & PWRTE_ON & MCLRE_OFF & CP_ON & CPD_OFF & BOREN_ON &
CLKOUTEN_OFF & IESO_ON & FCMEN_ON);
__CONFIG(PLLEN_ON & LVP_OFF); // Enable PLL
void init_fosc(void) {
OSCCON = 0xF0; // Set internal clock to 8MHz and enable 4X PLL
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
init_fosc();
while(1);
}
Understanding how to configure the clock is essential for optimizing performance and power usage in microcontroller applications. Whether you're working on a simple project or a complex system, choosing the right clock source and frequency can make a big difference in how your device operates.
Electrical Butt Connectors,Wire Terminal Connectors,Electrical Terminal Connectors,Spring Terminal Connector
Wonke Electric CO.,Ltd. , https://www.wkdq-electric.com