Note: This article is for beginners. Master can bypass! Why write an article? Although this issue is not worth mentioning to the electronic old white, but for the beginner MCU friends, there are too many people who ask this question. It has always been a sentence to explain to you, and the repeated work is really meaningless. It seems very necessary to talk about it here in a unified way. Since it is a beginner, we must briefly explain what the relay is.

(This is a relay that I have on hand.) The relay is a switch. The switch is controlled by its internal coil. The coil is energized, the relay is closed, and the switch is activated.
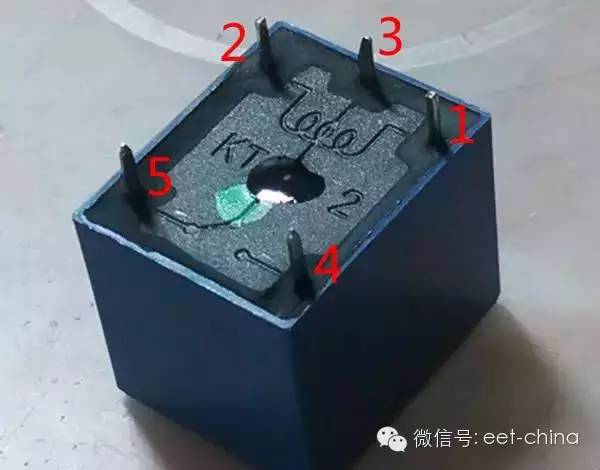

Some people also ask what is a coil? Look at the picture, pin 1 and pin 2 are on the two pins of the coil, pins 3 and 5 are now open, pin 3 and pin 2 are blocked. If you power up pin 1 and pin 2, you will hear a relay and then pin 3 and pin 4 will be on. For example, if you want to control the on and off of a line, you can deliberately disconnect this line. After one end is connected to pin 3 and one end is connected to pin 4, then you can control this line by turning on and off the coil. broken. How much voltage does the coil 1 and 2 add? This problem needs to look at the front of the relay you are using. For example, now I see this, you can see that it is 05VDC, so you can give 5V to the coil of this relay and the relay will pick up. How to increase the coil voltage? Finally came the question. You can directly use both hands to get 5V and GND two lines directly to the two pins of the relay coil, you hear the sound. How to use the microcontroller to give him voltage? We know that the microcontroller pin can output 5V. Is it possible to directly connect the relay coil with the microcontroller pin? The answer is certainly not. why? It does not matter whether it is the same or Ohm's law. You use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the relay coil.

For example, the resistance of my relay coil is about 71.7 ohms. If 5V is added, the current is 5 divided by 71.7 which is approximately equal to 0.07A, which is 70mA. Keep in mind that our microcontroller's normal pin outputs a maximum of 10mA, and the high-current pin outputs a maximum of 20mA (this can be seen in the microcontroller's datasheet). See it, although it is 5V, but the output current capacity is limited, can not reach the current to drive the relay, it can not directly drive the relay. At this time, you need to find a way. For example with the transistor S8050 drive. The circuit diagram is as follows.
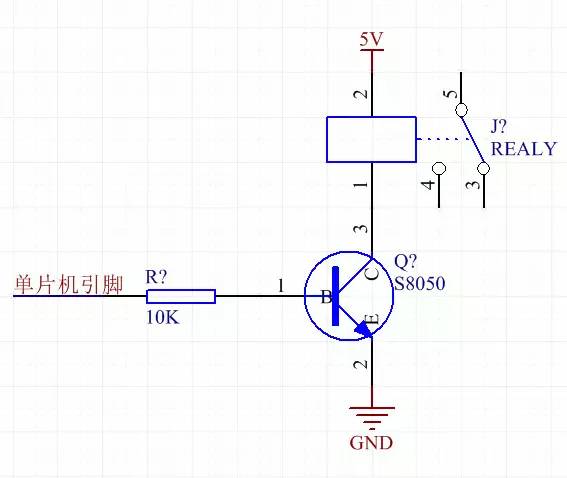
See S8050 datasheet, S8050 is an NPN tube, ICE maximum allowable current is 500mA, far greater than 70mA, so use S8050 to drive the relay is absolutely no problem. Looking at the picture above, ICE is the current flowing from C to E, which is the current of one line with the relay coil. NPN transistor, here is a switch, the microcontroller pin output 5V high, ICE will turn on the relay will pull; MCU pin output 0V low, ICE cut off, the relay does not pull. Similarly, the solenoid valve is also a very low-power load, and it is also necessary to select an appropriate drive element according to the above-mentioned Ohm's law. Do you understand?
Engine Parts Belt,Water Pump Belt,fan belt,dynamo belt
Chongqing LDJM Engine Parts Center , https://www.ckcummins.com