Transformers are devices that utilize electromagnetic mutual induction to change voltage, current, and impedance. Their primary functions include voltage transformation, current conversion, impedance adjustment, isolation, and voltage regulation (as seen in magnetic saturation transformers).
Commonly used transformers can be categorized as follows:
**Based on Cooling Method:**
1. **Dry-Type Transformers**: These transformers rely on air convection for cooling, either naturally or with added fans. They are typically employed in smaller capacity applications like high-rise buildings, highway toll booths, local lighting, and electronic circuits.
2. **Oil-Immersion Transformers**: These transformers use oil as their cooling medium. Types include oil-immersion self-cooling, oil-immersion air-cooling, oil-immersion water-cooling, and forced oil circulation systems.
**Based on Winding Structure:**
1. **Two-Winding Transformers**: These are used to connect two different voltage levels within the power grid.
2. **Three-Winding Transformers**: Often found in regional substations of the power system, they connect three voltage levels.
3. **Autotransformers**: These are used in power systems to connect different voltages. They can also function as regular step-up or step-down transformers.
**Based on Core Structure:**
1. **Core-Type Transformers**: These are typically used for high-voltage applications in power transformers.
2. **Amorphous Alloy Transformers**: Featuring an amorphous alloy core, these transformers represent a novel magnetic conductive material. They reduce no-load current by approximately 80%, making them highly energy-efficient distribution transformers, particularly suitable for rural power grids and underdeveloped areas where load rates are low.
3. **Shell-Type Transformers**: These are specialized transformers designed for high current applications, such as electric furnaces or welding transformers. They are also used in power transformers for electronic equipment like televisions, radios, and more, including models from Shanghai Hongzhi-box transformers.
In recent years, new terminal blocks for transformers have gained significant traction in global electrical and electronic engineering sectors. These terminal blocks are designed for large transformers and feature a structural design that facilitates easy wiring. Their screw connections are robust, allowing quick and convenient installation onto 2x10mm rails. The product’s design complies with international standards such as IEC 60947-7-1, ensuring compatibility and reliability across various applications.
Transformers continue to evolve, with advancements in materials and designs driving improvements in efficiency and functionality. This ongoing innovation ensures that transformers remain essential components in modern power systems, supporting everything from residential electricity needs to industrial operations worldwide.
The Powell lens resembles a round prism with a curved roof line. The lens is a laser line generator, stretching a narrow laser beam into a uniformly illuminated straight line.Powell Lenses, also known as laser line generating lenses, create straight, uniform laser lines by fanning out collimated beams in one dimension. Fan angles of 3°, 4°, 5°, 7°, 10°, 15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 75° etc are available.

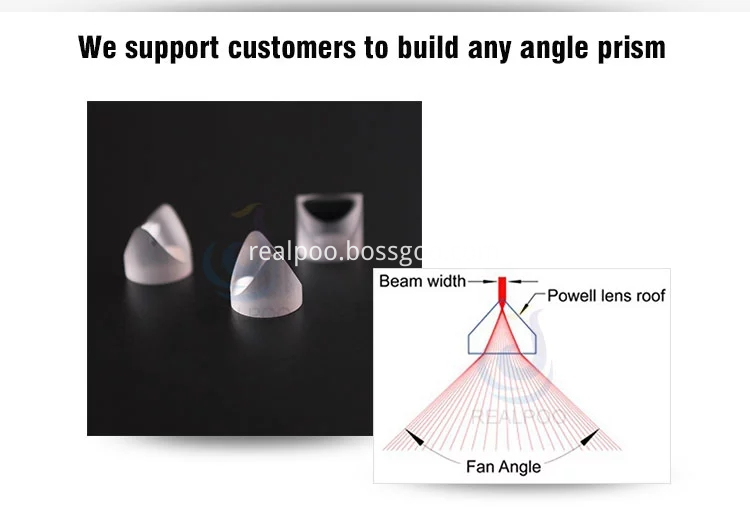


Powell Lens,Powell Lens Thorlabs,Angle Laser Line Generator Lens,Optical Gratings
Changchun Realpoo Photoelectric Co., Ltd. , https://www.optics-realpoo.com