 Australia is rich in solar energy, has a vast land resource, and the development of solar energy should have unique conditions. We also want to live in a solar-powered country. Indeed, in the past two years, our roof solar energy has developed rapidly, but if it comes to large-scale development, this country is still far behind.
Australia is rich in solar energy, has a vast land resource, and the development of solar energy should have unique conditions. We also want to live in a solar-powered country. Indeed, in the past two years, our roof solar energy has developed rapidly, but if it comes to large-scale development, this country is still far behind. So how far is it? Let's take a look at the recent British ambition of energy and climate change minister Craig Barker to repeat the British development ambitions. The UK plans to make the installed capacity of the domestic solar energy market reach 22,000 megawatts by 2020. Plans are currently underway to establish a large-scale solar power plant in Scotland, which is expected to begin as early as next year.
So what is Australia's plan? According to the White Paper on Energy Development Draft announced by the Australian government about a year ago, the installed capacity of solar energy in the future is planned to reach 3,000 megawatts. We should understand that this so-called plan can be achieved by the end of next year. Recently, the Australian Energy Department will issue a final development plan for this, and I hope that the target number can be adjusted. At the same time, specific plans for solar energy development, cost budgets, and future development paths should all be explained in detail.
The development of the solar energy industry is very critical for Australia, and the cost of rooftop solar is declining. But how can we promote the development of large-scale solar power plants? Last month, Australia launched its first commercial-scale solar power plant, the Greenough Solar Power Station. The Glenorne Solar Power Station is located in Walkawayville, Western Australia. It is operated by a joint venture between Virgin Energy of Western Australia and the United States General Electric Group. Its installed capacity is expected to reach 10 megawatts and it will provide 3,000 homes. Electricity. This has enabled the country to take another step towards achieving its ambitious goal of renewable energy use. The power plant is GE's first project to invest in the Australian renewable energy industry, and the company is considering expanding its installed capacity to 40 megawatts. According to reports, the Western Australia Water Company will purchase power generated by the power plant to supply a nearby desalination plant.
Virgin Energy Director Waters said: “The start-up of the Greenough Solar Power Plant demonstrates that renewable energy technologies will enable Australia’s future energy structure to be based on sustainable development and will be more cost-effective.†Although Australia’s development of solar energy has advantages that other countries cannot match, the prospects for the project are not bright, as some energy users and suppliers demand that the government reduce the country’s renewable energy production target. It is understood that Australia plans to increase its share of renewable energy production to 20% by 2020. At present, this ratio is 10%, of which 2/3 comes from hydropower.
In addition, the Australian Renewable Energy Development Plan has also received dissatisfaction from domestic coal and natural gas suppliers. Some large coal, natural gas companies, energy groups, and public agencies are obstructing efforts to reduce the mandatory development goals of renewable energy. At present, this target is undergoing routine review organized by Australia’s national climate change authority and it is expected that relevant work will be completed before the end of this year.
Proponents of renewable energy believe that cutting targets may destroy this emerging industry. According to the previously announced renewable energy goals, Australia is committed to increasing its share of renewable energy to 20% by 2020. Kane Thornton, director of strategy at the Australian Clean Energy Commission, said: "If the target is reduced or abolished, the renewable energy industry will fundamentally plummet and stagnate."
Although Australia enjoys superior conditions for the development of solar energy, Australia is lagging behind other countries in the development of large-scale solar power plants. Apart from the great difference with the United Kingdom, which countries are behind Australia?
Let's take a look at the development of solar energy in major global economies. The installed capacity of large-scale solar power plants currently built in the United Kingdom is 3,000 megawatts, and the target is 28,000 megawatts. China plans to increase the installed capacity of solar energy by 2015. 2.1 million megawatts, including distributed solar and large solar power plants. Why can China not develop solar energy on such a large scale, but Australia cannot? Because Australia is rich in energy and self-sufficient, if it is to develop renewable energy, the status of coal and natural gas will naturally decline.
Let's take a look again at India, an extremely energy-poor country that plans to have 20 million megawatts of solar installed capacity by 2022. At present, India has established several large-scale solar power plants and there are more plans in the future. The current installed solar capacity on rooftops in Germany, Spain and Italy is considerable. In addition, the number of commercial-scale solar power systems is also considerable. The current installed capacity of solar energy in Germany has exceeded 35,000 megawatts, and Spain is a major country with solar thermal power generation. Japan has already formulated a strong on-grid tariff subsidy policy and plans to develop solar energy on a large scale in the future to reduce its dependence on nuclear power.
As for other countries that are ahead of Australia, you may be surprised to say it. Including Ukraine, Bulgaria, Romania, the Czech Republic, France, Greece, Portugal, Peru, and Thailand have all been far ahead of Australia. Serbia recently announced the construction of a 1,000 megawatt solar park by 2016, while South Africa has signed an agreement to finance 600 megawatts of solar projects. It also plans to open tenders. Chile's current large-scale solar installation capacity is 3,000 megawatts, which is mainly established in the mining and mining concentration area.
In addition, there is Saudi Arabia, which has plans to spend 100 billion U.S. dollars to invest in 40,000 megawatts of large-scale solar power projects, so Saudi Arabia will have more oil for export and other purposes in the future. Last month, a Saudi official stated that Saudi Arabia is committed to making the country's power system 100% zero-carbon in less than a decade. At present, large-scale solar power stations are in full swing in the Middle East and North Africa. In the construction of the site, the project will be linked to the desert solar energy plan to deliver solar power to Europe. Australia is not dominant in the global large-scale solar energy industry, so there are still many issues to be done.
Cable Tray brackets are used to hold the cable tray and settle them in the position.Our brackets are made by the similar design which is wildly used in Japan and Euro products. It has the advantages of simple structures,little weights and strong strength; can fit the needs of different environments.
All the sizes and materials can be produced in our factory,always the most professional.
all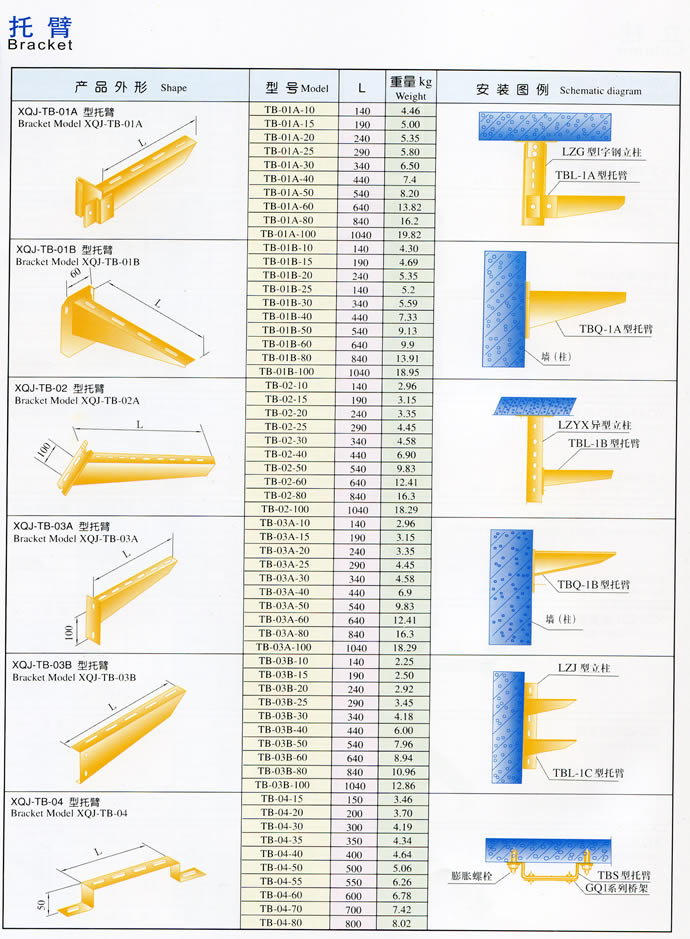
Cable Basket,Cable Tray With Bracket,Hanging Wire Mesh Cable Tray,Wire Basket Tray
Jiangsu Loncin Electric Equipment Co.,Ltd , https://www.loncincabletray.com